Objective: The purpose of this study was to assess the audiological results and surgical outcomes of patients who underwent endoscopic stapes surgery (ESS).
Methods: This study included 40 consecutive patients who underwent stapes surgery with a fully endoscopic approach at Dr. Ersin Arslan Research and Training Hospital between January, 2015 and April, 2018. We retrospectively evaluated the patients’ audiological results, surgery duration, surgical findings, and complications. To assess the learning curve, participants were divided into two groups based on their date of surgery: first twenty patients (FTPs) and last twenty patients (LTPs).
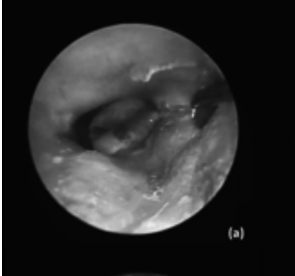
Results: The mean operative duration was 43.4 ± 11.3 minutes among all patients, 51.5 ± 9.2 minutes among FTPs, and 35.3 ± 3.9 minutes among LTPs (p < 0.05). The average air-bone gap (ABG) values were 33.7 ± 8.5 dB preoperatively and 8.7 ± 6.9 dB postoperatively (p < 0.05). The incudostapedial joint (ISJ) of 24 patients (60%) and the stapes footplate of 13 patients (32%) were directly visible without requiring bone curettage. None of the patients experienced major complications, such as facial paralysis or sensorineural hearing loss.
Conclusions: The present results show the surgical and audiological outcomes of exclusively endoscopic transcanal stapes surgery, indicating the advantages, limitations, and learning curve for this procedure. ESS appears to be a safe and effective alternative technique that produces reasonable surgical and functional outcomes.



.png)